Technology Exchange
We have been talking about induction brazing, so what exactly is induction brazing? Which manufacturer of high-frequency brazing equipment is more professional? Today, POLARIS-ETeK takes you to Know the specific situation of induction brazing!
Induction brazing is different from ordinary welding. The base material does not melt during brazing. It uses a solder with a lower temperature than the base material. The heating temperature is lower than the solidus of the base material and higher than the liquidus of the solder. When the connected parts and the brazing material are heated until the brazing material melts, it will dissolve and diffuse with the base material by capillary action and wetting effect, and then fill the gap between the base material and the connected parts.
|
|
| Pic1 | Pic2 |
Compared with brazing and fusion welding, brazing has the following advantages:
(1) The brazing heating temperature is low, which has little effect on the structure and performance of the base metal;
(2) The brazed joint is flat and smooth, with beautiful appearance;
(3) The deformation of the weldment is small, especially if the brazing method with uniform heating is adopted, the deformation of the weldment can be reduced to a minimum to ensure the dimensional accuracy of the weldment;
(4) High production efficiency;
(5) It can realize the connection of dissimilar metals or alloys, metals and non-metals.
If induction welding wants to be applied in practice, the following nine requirements must be met. Today we will talk about the first four points:
1. Introduction of induction welding solder
In order to meet the requirements of joint performance and brazing process, brazing filler metal generally meets the following basic requirements;
1) Suitable melting temperature range, under normal circumstances, its melting temperature is lower than that of the base material;
2) It has good wetting performance and spreading performance at brazing temperature, and can fully fill the joint gap;
3) The physical and chemical interaction with the base metal should ensure that they form a firm bond;
4) The composition is stable, minimize the burning or volatilization of the elements at the brazing temperature, and contain little or no rare metals and precious metals;
5) It can meet the requirements of physical, chemical and mechanical properties of brazed joints.
2. Introduction of flux for induction welding
The role of the flux is to remove oxides on the surface of the base material and the liquid solder, protect the base material and the solder from further oxidation during the heating process, and improve the wetting performance of the solder on the surface of the base material. Therefore, the flux must have sufficient ability to remove oxides on the surface of the base material and the solder; the melting temperature and the lowest active temperature should be slightly lower than the melting temperature of the solder, and have sufficient wetting ability at the brazing temperature.

Pic3
3. The fit gap of induction welding In the brazing process
the choice of joint gap is very important. A reasonable joint gap is not only related to the capillary action of the molten solder, and then affects the flow in the weld, but also the structural formula formed by the solidification of the molten solder in different gaps is different. In the case of a large gap, the crystal grains will grow without directionality, which will affect the strength of the joint; when a small gap is used, there is a layer of crystal grains along the width of the brazing joint, the gap is reduced, and the amount of solidified metal is reduced. , So that smooth flat crystal grains can be formed after solidification, and the weld strength is improved. According to the material of the workpiece and the selected brazing filler metal, the gap of the liquid-dispensing joint welding is selected from 0.05 mm to 0.15 mm, which can give full play to the capillary function and ensure the strength of the weld joint.

Pic4
4. Pre-welding treatment for induction welding Before brazing
the oxides, grease, dirt, etc. on the surface of the workpiece must be carefully removed, because the molten solder cannot wet the surface of the uncleaned parts, nor can it fill the joint gap. Cleaning the surface of the part includes: Clean up oil stains: oil stains can be removed with organic solvents. Commonly used organic solvents are alcohol, carbon tetrachloride, gasoline, trichlorinated alkene, dichloroethane and trichloroethane, etc. Removal of oxides: Mechanical methods can be used to remove oxides on the surface of parts, such as files, metal brushes, sandpaper, sandblasting, etc.; chemical erosion methods; electrochemical erosion methods.

Pic5
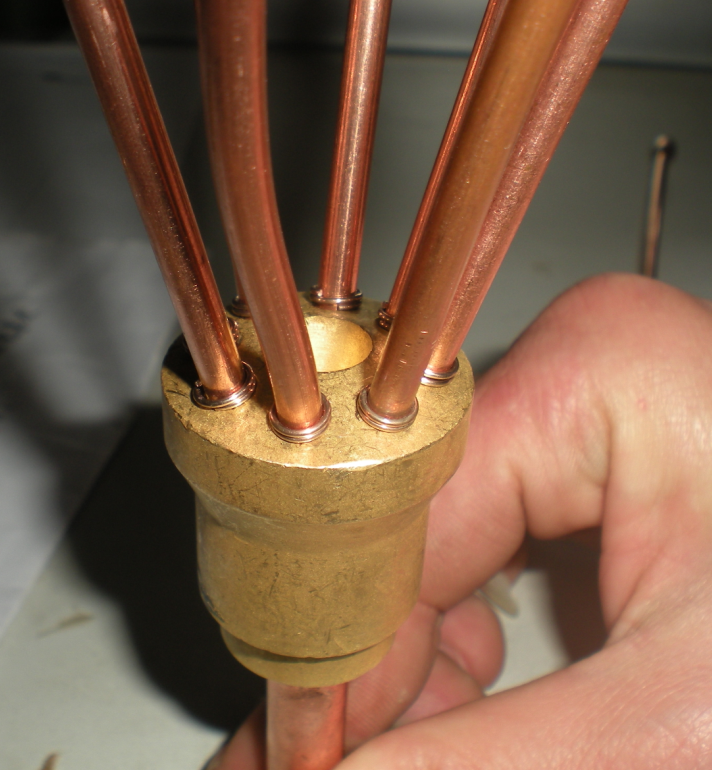
Real cases of induction brazing:
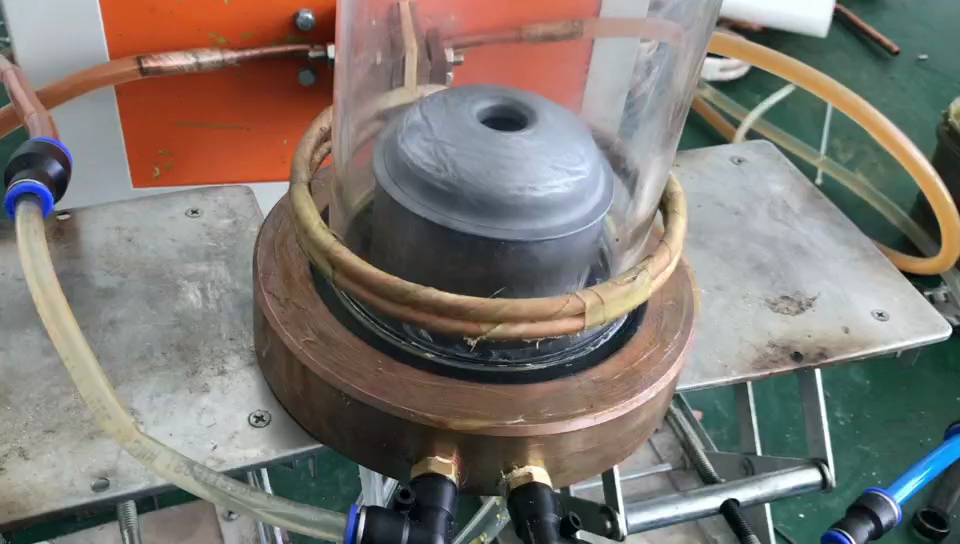

Pic6
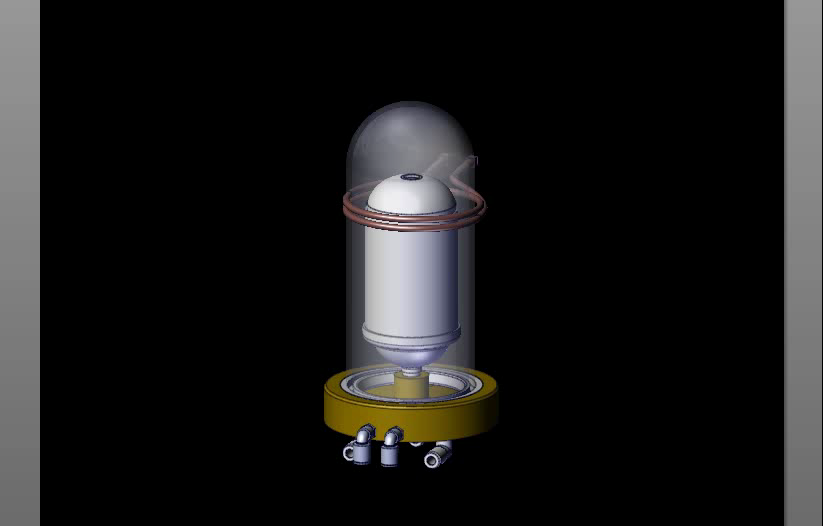
Induction vacuum brazing
More News on POLARS-ETeK, Welcome to consult and leave a message.



 Scan and follow!
Scan and follow!