Technology Exchange
Yesterday POLARIS-ETeK talked about the first four points that should be paid attention to when using induction brazing. Today we will talk about the remaining five points that need to be noted yesterday.
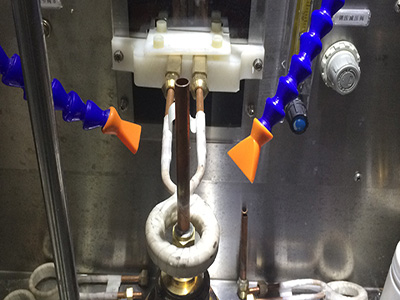
5. Assembly and positioning of induction welding
There are many ways to fix parts by brazing. For parts with small size and relatively simple structure, we can use simple fixing methods, such as relying on dead weight, tight fit, spring clips, positioning pins, etc.
For parts with complex structures, special fixtures are generally used for positioning. The requirements for brazing fixtures are also very strict. The fixture should have good high temperature resistance and oxidation resistance, the thermal expansion coefficient of the fixture parts should be similar, the fixture should have sufficient rigidity, but the structure should be as simple as possible, and the size should be as small as possible In this way, the work of the fixture is both reliable and efficient.
 |  |
| Pic1 | Pic2 |
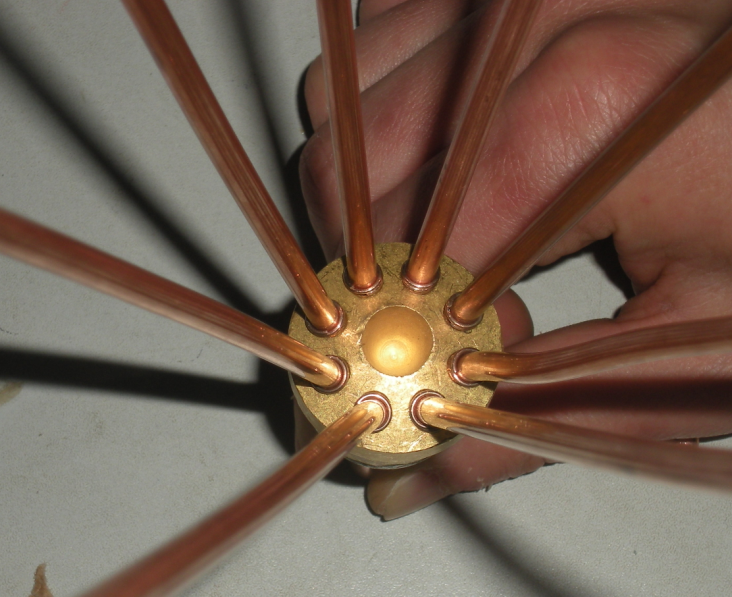
6. Solder placement for induction welding
Most brazing should be pre-installed on the joint before starting work. When placing the brazing material, the gravity effect of the brazing material and the capillary action of the gap should be used as much as possible to promote the brazing material to fill the gap. The brazing material must be used Close to the joints to suck into the gap by capillary action. For the joints with tight fit and large overlap length, the brazing filler metal placement groove should be opened on the joint.
Pic3
7. Flux coating for induction welding
In order to increase the fluidity of the solder, it is sometimes necessary to apply flux. Flux is the flux used in brazing. Its role is to remove oxides on the surface of the brazing filler metal and base metal, and to protect the weldment and liquid filler metal from oxidation during the brazing process, and to improve the performance of the liquid filler metal on the weldment. Wettability.

Pic4
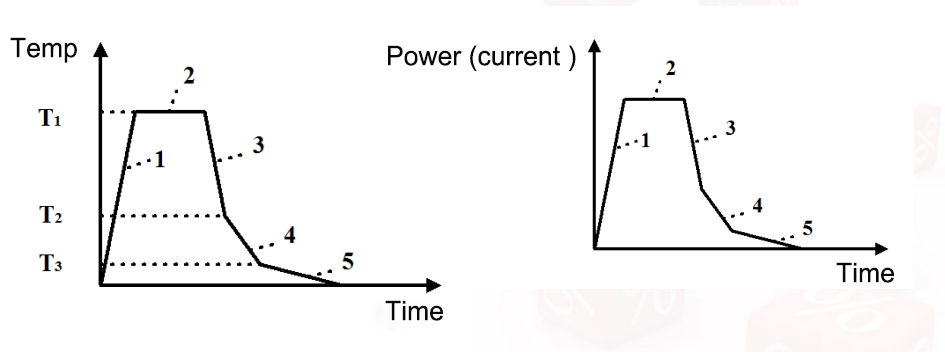
8. Process parameters of induction welding
The main technological parameters of the brazing process are the brazing temperature and holding time. The brazing temperature is usually selected to be 25-60°C higher than the liquidus temperature of the solder to ensure that the solder can fill the gap, but sometimes there are exceptions. For example, for some brazing filler metals with a wide interval of crystallization temperature, since a considerable amount of liquid phase exists below the liquidus temperature, it has certain fluidity. At this time, the brazing temperature can be equal to or slightly lower or slightly lower than the liquidus temperature of the solder.
Pic5
The holding time of brazing depends on the size of the workpiece and the intensity of the interaction between the brazing filler metal and the base metal. The heat preservation time of large parts should be longer to ensure uniform heating. If the brazing filler metal has a strong effect on the base material, the heat preservation time should be short. Generally speaking, it is necessary to promote the mutual diffusion of the brazing filler metal and the base material during a certain holding time to form a firm bond, but an excessively long holding time will cause defects such as dissolution.
9. Cleaning after induction welding
The cleaning work after the last step is indispensable. Most of the flux residues have a great corrosive effect on the brazed joints, and also hinder the inspection of the weld. Therefore, it needs to be cleaned up, but the flux rosin will not have a corrosive effect. No need to clear.
The rosin-containing active flux residue is insoluble in water and can be removed with organic solvents such as isopropanol, alcohol, gasoline, and trichloroethylene. The flux composed of organic acid and salt is generally soluble in water and can be washed with hot water. The flux composed of inorganic acid is soluble in water and can also be washed with hot water.
The borax and boric acid flux residues used for brazing are basically not soluble in water and difficult to remove. Generally, sandblasting is used to remove them.
Field case
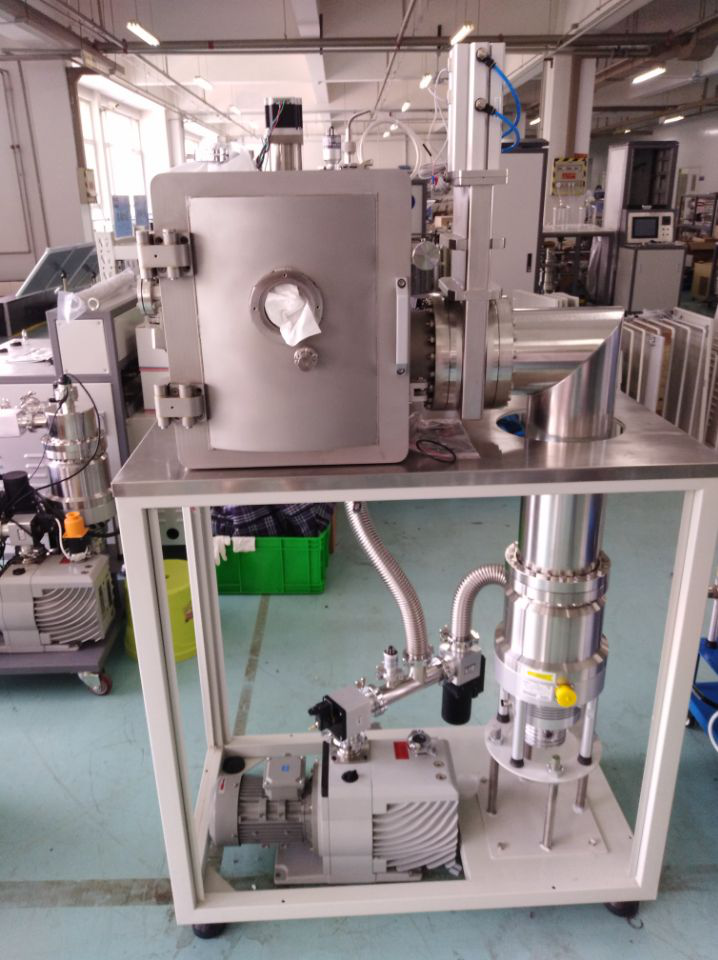

Pic6
After reading POLARIS-ETeK’s two introductions on induction brazing, I think everyone should know the basic use and precautions of induction brazing equipment, so if you have any other questions, please leave a message.


 Scan and follow!
Scan and follow!